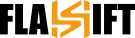
Technical Analysis for Crypto Trading | Success in cryptocurrency trading, which moves quickly, is estimated not to be achieved intuitively but to demand a strategic approach. Technical Analysis for Crypto Trading is a valuable tool that enables traders to make well-informed decisions based on the historical record of past price movements, chart patterns, and trading volumes. Using various indicators and techniques, it is designed to indicate market trends, possible reversals, and points of entry or exit. Therefore, it becomes an indispensable skill for anyone who wants to confidently enter the highly volatile cryptocurrency market. This guide considers how to use technical analysis effectively in improving your crypto trading strategy.
For exchange cryptocurrency at the best rate, visit Flashift website, create a registration-free transaction and take advantage of a secure and speedy experience.
Introduction to Technical Analysis
The cryptocurrency market is volatile and full of opportunities and risks. To succeed in this dynamic environment, traders should have at least one reliable strategy to support their decision-making. Technical Analysis for Crypto Trading describes a well-structured plan for analyzing past price behavior and market data to forecast future prices.
We will discuss technical analysis, how it works, and why it is essential to any serious crypto trader.
What is Technical Analysis?
Technical analysis is how traders determine price movements to predict their futures based on past market data, primarily through price and volume. In contrast to fundamental analysis, which estimates the actual value of an asset with its technology, team, or adoption rate, technical analysis strictly deals with chart patterns, trends, and statistical indicators.
Technical analysis studies observe statistical trends and patterns in a cryptocurrency’s price movement. The underlying assumption of technical analysis is that all information relevant to a cryptocurrency’s value is reflected in its price. Therefore, observing patterns and using various tools and indicators can predict the up- or down-movement price.
Why Technical Analysis is Essential in Crypto Trading?
Being speculatory, cryptocurrency markets are particularly vulnerable to extreme wild price swings. But this unpredictability makes technical analysis so essential to the crypto trader. Here’s why:
- Market behavior reflects sentiment: In the crypto market, sentiment and psychology are essential to price movement. Technical analysis helps traders identify trends and possible turning points that show shifts in market sentiment.
- Short-term trading opportunities: Most cryptocurrency traders engage in short-term trades, taking advantage of fast price changes. Technical analysis becomes essential for deciding the perfect entry and exit for a trade, enabling swift and well-informed decisions.
- The high volatility in crypto trading requires some risk management. Technical analysis helps traders set stop-loss levels and limit orders to reduce potential losses from surprise downturns.
Key Concepts of Technical Analysis for Crypto Trading
Technical analysis is based on a few concepts. Master them, and it will be easy to apply in cryptocurrency trading.
- Trends
Trends show the direction in which, as a general rule, changes in the price of a cryptocurrency move. There are three types of trends:
- Uptrend: Prices keep on going up.
- Downtrend: Prices are falling all the way.
- Sideways Trend: Price moves within a range without any direction.
It enables the trader to comprehend the broad market perspectives while deciding based on the overall market move.
- Support and Resistance Levels
- Support: The level at which a cryptocurrency finds buying interest to prevent further decline.
- Resistance: A level where selling pressure tends to emerge, preventing the price from rising.
These levels help the traders identify price reversal points and decide on placing buy or sell orders.
- Chart Patterns
Chart patterns are graphical analyses of price movements that signal a probable reversal or continuation of an ongoing trend. Some usual patterns are:
- Head and Shoulders: A chart pattern signaling that a reversal in action has occurred in a trend.
- Double Tops and Bottoms: These are chart patterns at the end of an uptrend or downtrend.
- Triangle: Formations that can predict a breakout either upwards or downwards.
Being in a position to spot these patterns puts the trader ahead of price movement, and such decisions are made with confidence.
- Technical Indicators
Indicators are tools of mathematics based on their price, volume, or open interest data. Commonly used indicators include:
- Moving Averages (MA): The mean of a cryptocurrency’s price is calculated over a fixed period, smoothing out short-term fluctuations.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): This index indicates the speed and change of price movement that shows overbought or oversold conditions.
- MACD—Moving Average Convergence Divergence—is a trend-following indicator that helps identify momentum and possible reversals.
These indicators confirm price trends and give buy or sell signals.
The Role of AI in Modern Technical Analysis
he adoption of AI and ML is transforming technical analysis by enabling the processing of vast datasets to identify patterns and predict market movements with increased accuracy. These technologies facilitate the development of sophisticated trading algorithms that adapt to changing market conditions in real-time. For instance, AI-driven platforms can analyze historical price data alongside real-time market sentiment from social media and news sources, providing traders with comprehensive insights. This integration allows for more informed decision-making and the automation of complex trading strategies, reducing the cognitive load on traders.
Read More: AI in Cryptocurrency Trading: Opportunities and Risks
Benefits of Using Technical Analysis in Crypto Trading
- Data-Driven Decisions: Technical analysis utilizes available market data to make a trading decision, eliminating emotion-oriented trading bias.
- Swift Market Sentiment Analysis: The trader’s study of chart patterns and indicators allows for a quick market sentiment analysis, enabling better decisions.
- Improved Risk Management: Technical analysis allows traders to protect their capital in the market through stop-loss and limit orders.
- Timeframe Flexibility: Technical analysis can be applied to any time frame, whether you day trade or take a long-term approach.
So…
Therefore, technical analysis for crypto trading is one of the most capable tools for helping a trader confidently enter the cryptocurrency market. The key concepts in understanding and applying trends, support and resistance levels, chart patterns, and technical indicators will help traders make more data-driven and informed decisions. While it does not promise success, technical analysis optimizes your chances for better trade profitability and efficient risk management.
For exchange Ethereum (ETH) to Tether (USDTERC20) in one second, Flashift is the easiest way.
Key Indicators and Tools for Crypto Trading
The crypto market is highly volatile, hence equally challenging and rewarding for a trader. Traders depend on technical analysis for crypto trading to survive in this complex market, wherein past price data and market behavior are used to predict forward price movements. Indicators and tools are at the heart of technical analysis, which will help the trader identify trends and reversals and trade entry and exit.
Here, we will examine some essential indicators and technical analysis tools for improving a crypto trading strategy.
-
Moving Averages (MA)
Moving averages (MAs) are among the most commonly used indicators in technical analysis. They soften the price data to help identify trends by averaging the price of a cryptocurrency over a certain period.
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): The SMA calculates the average price over a set period (e.g., 50 days, 200 days). It helps traders spot long-term trends and filter out short-term noise.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): The EMA gives more weight to recent price data, making it more responsive to new price information. This is particularly useful for short-term traders looking to capture quick price movements.
How to use: The moving averages reflect the bigger picture of the cryptocurrency trend. If the price is above the MA, this is considered an uptrend; if it is below, it is a downtrend. Typically, longer and shorter moving average crossovers- the so-called golden crosses- form when the 50-day MA crosses above the 200-day MA and can give potential buy or sell signals.
-
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed of a price change over usually 14 days. Its readings range from 0 to 100.
- Overbought: An RSI above 70 suggests that a cryptocurrency is overbought, meaning its price may be too high and be due for a correction.
- Oversold: An RSI below 30 indicates that a cryptocurrency is oversold, meaning its price may be undervalued and could experience a rebound.
How to use: The RSI detects potential reversal levels. On extreme levels, overbought-oversold traders expect a price correction if the RSI is overbought and a price bounce if it is oversold.
-
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
MACD is a trend-following indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of the price of a cryptocurrency. It consists of two lines:
- MACD Line: The difference between the 26-day EMA and the 12-day EMA.
- Signal Line: A 9-day EMA of the MACD Line.
The MACD generates trading signals when the two lines cross:
- Bullish Crossover: When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it may indicate a buying opportunity.
- Bearish Crossover: When the MACD line crosses below the signal line, it may suggest a selling opportunity.
How to use it: MACD shows the trader the change in momentum and confirms trends. It helps find possible reversals in a trend.
-
Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are volatility indicators that consist of three lines:
- Middle Band: A moving average of the cryptocurrency’s price.
- Upper Band: A-line two standard deviations above the middle band.
- Lower Band: A-line two standard deviations below the middle band.
Since the movement towards the upper band approaches the price, the price may be overbought, and when the movement approaches the lower band, it may be oversold.
How to use: Bollinger Bands helps identify periods of volatility contraction and expansion. When the bands tighten – what has come to be known as a “squeeze” – it is a warning that the volatility is about to increase, and when the bands widen, saying that volatility has increased and the price is overdue for a correction.
-
Fibonacci Retracement
The Fibonacci Retracement tool is based on the Fibonacci sequence and tries to predict a possible level of support and resistance during a trend. The idea is to assist traders with guessing at which level prices might reverse in a correction.
The standard Fibonacci retracement levels are 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%. These levels were considered potential support areas during an uptrend and resistance during a downtrend.
How to use: Traders use Fibonacci retracement levels to establish the key points at which the price might reverse or continue a particular trend. In any correction, for example, the price may find support at the 61.8% retracement level and continue upward in its trend.
-
Volume Indicators
Volume is a substantial element in technical analysis, informing about the level of interest in cryptocurrency. To analyze the strength of a price move, one can make use of several volume-based indicators:
- OBV: It is a volume flow indicator that predicts price changes. When a cryptocurrency trend increases with the rise in OBV, it confirms a strong trend.
- Volume Profile: This profile depicts the volume traded at each price level. It helps traders trace the support and resistance zones where high buying/selling activity usually concentrates.
How to use: Volume is heavy in an up-trend of price, reflecting heavy buying pressure; similarly, volume is heavy in a down trend of price, reflecting heavy selling pressure. Indicators of volume confirm the validity of trends and possible reversals.
-
Stochastic Oscillator
One of the momentum indicators is the Stochastic Oscillator. This indicator compares the closing price of a cryptocurrency with its range over a period. Its readings vary from 0 to 100.
- Overbought: A reading is overbought when it is above 80, meaning the price may fall at any moment.
- Oversold: When values fall below 20, this signals oversold conditions, suggesting higher prices may be expected.
Use: Like the RSI, this stochastic oscillator indicator identifies possible reversal levels. When traders reach either extreme, they seek a change in the direction of the cryptocurrency’s price.
-
Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick charts are one of the essential tools of technical analysis, starting from the custom when each candlestick implies some period and shows the opening, closing, high, and low prices. Candlestick patterns give a visual cue about market sentiment and possible price reversals.
- Bullish Engulfing: This pattern shows buyers are taking over, which marks the beginning of an uptrend.
- Bearish Engulfing: The sellers overpower the buyers, which could indicate a potential downtrend.
Usage: Known candlestick patterns help traders predict market fluctuations. Candlestick analysis, along with another technical analysis tool, fortifies trading signals.
In Conclusion
Key indicators and tools are necessary to master technical analysis for crypto trading. Moving averages, RSI, MACD, Bollinger Bands, Fibonacci retracement, volume indicators, stochastic oscillators, and candlestick patterns can be essential inlets into better decision-making while taming the cryptocurrency market’s inherent volatility.
Each of these tools provides different insights into market conditions. Together, they offer a broad-based view that helps traders optimize their entry and exit, manage risk, and maximize profits.
Reading and Interpreting Crypto Charts
Reading and interpreting charts are key to making correct trading decisions regarding volatile cryptocurrencies. Crypto Technical Analysis uses historical price data to identify patterns and trends that help predict future price movements. This approach is based on effectively using crypto charts, which visually represent market data. Reading these charts is one of the primary skills required for serious crypto trading.
The following section examines crypto chart basics, key patterns, and important indicators that help traders understand market movements.

Types of Crypto Charts
Mainly, it is vital to learn the various types of crypto charts that traders make use of before setting eyes on chart analysis:
- Line Chart: This is the most basic type of chart. In a line chart, the closing prices for a stock or series are connected over time. While a line chart provides an instant impression of the basic trend in a price, it does not portray detailed information such as intraday price movements.
- Bar Chart: The bar chart is more informative as it displays the opening and closing high and low prices in a period. Each vertical line shows a range of prices, while horizontal lines specify the opening and closing prices.
- Candlestick Chart: The most used chart in crypto trading, candlestick charts intuitively visualize price action over time. Each candlestick represents a certain period and shows the opening, closing, and high and low prices. This format allows traders to get an overview of market patterns and trends.
Understanding Candlestick Charts
Candlestick charts are essential tools in technical analysis for crypto trading because they represent the complete view of market sentiment in every trading period. Here’s how to read them:
- Body: The body of a candlestick shows the price difference between the opening and closing prices. If the candle’s color is green or white, the closing price will be higher than the opening; therefore, a bullish trend is followed. If the color is red or black, the closing price is lower than the opening price; thus, a bearish trend has occurred.
- Wicks/Shadows: The lines above and below the body denote the highest and lowest prices reached during the period. Extending the wicks indicates significant volatility, with prices moving considerably higher or lower than the open and closed prices.
- Candle Size: The size of the body and wick can indicate the vigor or strength of a market. A long body indicates intense buying/selling pressure, while short bodies indicate indecision or lack of momentum.
Identifying Key Chart Patterns
Technical Analysis in crypto trading is a pattern identification that indicates either a reversal or a continuation of an underlying trend. Some commonly observed patterns include the following:
- Trend Reversal Patterns
- Head and Shoulders: This reversal pattern typically appears at the top of an uptrend. It contains three peaks: a head, the highest of the three, and two shoulders. When the price breaks below the neckline, which forms the support, it signals a bearish reversal.
- Double Top and Double Bottom: The pattern of Double Top is developed after an uptrend, with a sequence of bearish reversal. The development of Double Bottom is after an uptrend, with a potential bullish reversal. Such patterns are “M” for a double top or “W” for a double bottom. Such signals reveal the direction shift in the course of the trend.
- Trend Continuation Patterns
- Triangles: Represent areas of price contraction where the movements are confined within areas of contracting range up to breakout. The triangles are three:
- An ascending triangle, during an uptrend, is a bullish continuation;
- Descending triangle, during a downtrend, shows further losses;
- The symmetrical triangle is indecisive since the breakout can occur in either direction.
- Flags and Pennants: Both show short-term consolidation, continuing the current trend. A flag is rectangular, while a pennant looks like a small triangle. These patterns often lead to a breakout in the direction of the previous trend.
Support and Resistance Levels
One of the most essential concepts in Technical Analysis for Crypto Trading is knowing the level of support and resistance. These are significant price levels at which the tendencies of cryptocurrency have reversed or come to a stop.
- Support: The price level at which demand is sufficient to prevent the price from falling further. When a price approaches support, the rate often bounces back up because buyers generally step in.
- Resistance: A price level at which selling pressure prohibits the further rise of a price. Resistance is the price level where the price is turned around or consolidated when approached because sellers have come into play.
Traders use these support and resistance levels to determine potential entry and exit points and to indicate where the market may retreat.
Last Words…
Reading and interpreting crypto charts is the most critical skill in crypto trading. Understanding candlestick charts, identifying key patterns, and using technical indicators can help you make the best decisions and stand a better chance of guessing subsequent price movements. By effectively using Technical Analysis for Crypto Trading, you will develop a strategic approach to navigating the ever-changing cryptocurrency market, helping you manage risk and optimize your trading opportunities.
Common Technical Analysis Strategies
Technical analysis is critical in crypto trading to predict the market’s past prices. Traders typically adopt indicators and price action strategies to read patterns and predict future price trends. This includes using Moving Averages, the Relative Strength Index, and price actions such as Return to Mean, Inner Circle Traders, and Smart Money Concepts.
Technical Indicators
Moving Averages (MA) Strategies
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): The SMA is the average of the prices of a crypto asset over a certain period, usually over 50 or 200 days. It smooths out short-term fluctuations and shows the trend behind the price.
- Strategy: Traders use the crossover strategies, the Golden Cross, where the 50-day SMA crosses over the 200-day SMA, as an indication of the beginning of a bull run, and the Death Cross, where the 50-day SMA crosses below the 200-day SMA to form a bearish signal.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): The EMA prioritizes the most recent price data, making it more responsive to the latest information than the SMA.
- Strategy: Traders rely on short-term EMAs, like the 12-day, versus longer-term EMAs, like the 26-day, to produce buy and sell signals. A bullish signal is given when the short-term EMA crosses above the long-term EMA, and vice-versa for a bearish signal.
Relative Strength Index (RSI) Strategies
The RSI is an oscillator that moves between 0 and 100. It measures the magnitude of recent price changes to determine overbought or oversold positions in assets. Strategy: If RSI exceeds 70, the asset is overbought, which may signal positioning for a sell-off or price correction. If the RSI falls below 30, the asset is said to be oversold, which could be a good time to buy.
Traders often combine RSI with trendlines or moving averages to confirm the signal and avoid false positives.
Price Action Styles
Price action strategies depend on interpreting price movements, which is done with limited use of indicators. These strategies are based on market structure, trends, and patterns.
1. Read The Market (RTM) Strategy
RTM is based on the premise that prices will revert to the mean or “average” over time. After significant deviations, the asset will often self-correct to the historical average.
Strategy: Any trader following the RTM strategy would look to take advantage of a situation where an asset is extended too far up or down from its long-term mean and is thus due for a mean reversion. Typically, traders using such a strategy would consider an asset overbought or oversold based on a moving average, Bollinger Bands, or price channels.
2. Inner Circle Trader (ICT) Strategy
ICT trading is the process of comprehending institutional market behavior and the areas of liquidity. Accordingly, in ICT trading, “trading like the smart money” is identified through understanding the key liquidity pools or, more simply, the areas where institutions enter or exit a position.
Strategy: ICT traders seek signs of liquidity grabs around significant highs or lows. They employ order blocks, or areas of institutional buying/selling, to define an area of interest where the price may reverse.
Entry and exit notably include the FVG and market imbalances, wherein the price will most likely fill those gaps.
3. Smart Money Concept – SMC Strategy
SMC is similar to ICT but more organized in defining market behavior through institutional techniques. It focuses on how “smart money” (institutional traders) manipulates price movements to capture liquidity.
Strategy:
- Traders focus on the market structure, finding higher highs and lower lows and breaks in the market structure to bring entry/exit points.
- Order Blocks: Like in ICT, SMC traders define zones where massive institutions place buy/sell orders.
- Liquidity Zones are areas where traders expect the price to “grab liquidity” (e.g., stop-loss levels) before the reverse.
- Mitigation Blocks: These blocks indicate where the smart money is changing its position or adjusting orders based on the current market conditions.
Combining Indicators with Price Action
One potent combination combines indicators such as RSI or MA with price action techniques from RTM, ICT, or SMC to get a wholesome market view. Example:
- RSI + SMC: To refine entries and exits, use RSI for overbought and oversold conditions and SMC for market structure and liquidity zones.
- EMA + RTM: The EMA efficiently defines a dynamic mean to which traders will see reversions after sharp deviations.
If implemented effectively, these could prove a robust set of tools for the crypto trader in pinpointing profitable opportunities and controlling risk in a highly volatile market.
Combining Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Successful trading of ever-evolving cryptocurrency markets requires more than just an eyebrow on the price charts and technical indicators. While Technical Analysis for Crypto Trading is very enlightening in terms of the trends of prices and behaviors of the market, it’s always better to add fundamental analysis to get a fuller picture of the potential an asset holds. These two merged approaches can bring perfection to a trader’s decision and, ultimately, his success rate.
We’ll see how technical and fundamental analysis can be combined to present a more robust trading strategy, plus the best way to incorporate such methodologies.
Understanding Technical and Fundamental Analysis
- Technical Analysis
Technical Analysis studies price graphs, patterns, and technical analysis indicators to arrive at future price movements from historical data. The key aspects of technical analysis are:
- Price Charts: These are line, bar, and candlestick charts showing prices in graphical representation.
- Indicators: This will include Moving Averages, RSI, and MACD to spot trends, momentum, and potential reversal points.
- Chart Patterns: Head-and-shoulders, Double Tops, and Triangles are visible and may indicate further moves.
Technical analysis studies market sentiment and price action using past price databases to make forecasts.
- Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental Analysis is the study of the elemental forces of demand and supply that determine the value of an asset. Cryptocurrencies will include project fundamentals, such as technology, use case, development team, and overall vision of the cryptocurrency project.
- Market Demand: The adoption rate, partnerships, and real-world cryptocurrency applications.
- Economic and Regulatory Factors: Government regulations, economic conditions, and market news influence the value of cryptocurrency.
- Tokenomics deals with cryptocurrencies’ supply and demand dynamics, including the total supply, circulation, and issuance schedules. Fundamental analysis can provide insight into a cryptocurrency’s intrinsic value and long-term potential.

Combining Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Merging the two aspects, technical and fundamental analyses, allows traders to create a more subtle way of trading. Here’s how one can merge the two approaches effectively:
- Start with Fundamental Analysis
Do a proper fundamental analysis that reveals its current value and prospect by determining the following focuses:
- Technology and Innovation: Assess the cryptographic technology on which the cryptocurrency is based and compare it to competitors in terms of scalability, security features, and technological innovation.
- Team and Development: This involves researching the development team’s experience, track record, and commitment to the project.
- Adoption and Use Case: Understand the cryptocurrency’s real-world applications, the partnerships and markets it has been adopted into, and its potential future growth.
- Market Sentiment and News: Stay updated on recent regulatory developments, market news, and economic factors that are likely to affect the value of cryptocurrency.
This foundational understanding helps identify cryptocurrencies with strong, long-term potential and contextualizes technical analysis.
- Timing with Technical Analysis
After selecting promising cryptocurrencies with the help of fundamental analysis, you will need technical analysis to time entry and exit. Key considerations should include:
- Trends in Prices: Study the price graphs and moving averages to identify current trends and probable reversals. Look for convergence between the cryptocurrency’s fundamental strength and the technical viewpoint, which indicates a good entry point.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Identify chart patterns, such as levels of support and resistance, Heads and Shoulders, and Triangles, that can indicate future price movements. Combining this with fundamental insight would be helpful when confirming your trading decisions.
- Momentum Indicators: Recognize RSI, MACD, and Bollinger Bands for market momentum measures and trend confirmation. This will be where the technical signals you get align with the fundamental insights to help boost confidence in trade decisions.
- Watch Market Conditions
You can keep yourself updated on technical and fundamental factors affecting your trade. For example,
- News and Events: Major news events or any change in regulation can affect the fundamentals of the cryptocurrency. Sudden news events can cause price changes, influencing your technical analysis.
- Market sentiment: Observe general market sentiments and investor behavior. Fundamental changes in sentiment can come through new partnerships, technological advancements, or other events that may affect market trends and technical patterns.
-
Be Prepared for Changing Your Strategy
The cryptocurrency market is very volatile. From both the technical and fundamental analysis perspectives, many factors can change in the blink of an eye. Revisit your strategy regularly in light of the following:
- Main events: Update your fundamental analysis regarding new information, updates on projects, or changed market circumstances. Could you update your investment thesis accordingly?
- Technical signs: Assess indications given by technical analysis and chart patterns to adjust your trading strategy continually. This will allow you to change this setup when it alters.
Case Study: Applying Combined Analysis
Now, consider you are studying a cryptocurrency project with excellent fundamentals-innovative technology, a reputable team, and considerable market adoption. You feel through fundamental analysis that the project has good long-term potential. Now, you want to use technical analysis to refine your trading strategy:
- Identify Key Levels: Using price charts, you draw key support and resistance levels that can affect price movements.
- Trend Following: The moving averages and RSI are some technical indicators confirming this is a strong momentum uptrend.
- Chart Pattern Identification: Chart patterns can paint a potential breakout or consolidation. You need to correlate those with fundamental insights to confirm your trade.
Applying technical and fundamental analyses gives you a complete picture of the potential cryptocurrency and makes wiser trading decisions.
How Retail Traders Can Benefit from Advanced Tools
The landscape of crypto trading is evolving rapidly, with more sophisticated tools becoming accessible to retail investors. Traditionally, advanced trading features—such as futures contracts, algorithmic trading, and in-depth technical indicators—were reserved for institutional investors. However, modern trading platforms are now offering retail traders access to professional-grade analytics, automated trading bots, and AI-powered market insights.
Many brokers and exchanges have introduced features like customizable charting tools, real-time market sentiment analysis, and advanced order types, enabling individual traders to execute more precise and strategic trades. Additionally, mobile trading apps have improved significantly, allowing traders to monitor and act on market movements instantly. By leveraging these powerful tools, retail investors can enhance their technical analysis approach, making more informed trading decisions in an increasingly competitive crypto market.
So…
Crypto trading involves combining technical and fundamental analysis. While technical analysis provides insight into price trends and trade prospects, fundamental analysis helps one understand a cryptocurrency’s value and long-term potential. Thus, combining such approaches into an integrated methodology allows one to create a more proficient and valid trading strategy, enhance one’s decision-making process, and improve one’s success rate in dynamic cryptocurrency trading.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a helpful tool in the fast-paced and often unpredictable world of cryptocurrency trading. Traders use indicators and chart patterns to analyze historical price data and predict future price movements and the best entry and exit points. However, technical analysis is imperfect and can lead to potential mistakes.
In doing so, we will identify some of the most flagrant errors in technical analysis and show ways to avoid them in your effort to make more relevant and successful trading decisions.
-
Over-reliance on Technical Indicators
The most common mistake in technical analysis is overreliance on technical indicators. While indicators like Moving Averages, RSI, and MACD are fine tools, they should not be relied upon as standalone means.
Pitfall: Indicator-Only Trading
Too many traders base their trading decisions exclusively on technical indicators without considering anything else. Indicators can give conflicting signals and do not always precisely mirror what is happening in the market.
Solution: Using Indicators within a Context
An effective way to avoid this pitfall is to combine multiple indicators and use them with price action and chart patterns. For instance, you may use Moving Averages to identify trends, RSI to measure momentum, and MACD to identify potential reversals. Please look at the broader market context, including news events and fundamental factors that validate your technical analysis.
-
Ignoring Market Context and Fundamentals
Technical analysis sometimes only accounts for prices, but it becomes incomplete without considering the broader market context and fundamental factors.
Pitfall: Avoiding Market News and Events
Market news, regulatory changes, and macroeconomic events might significantly affect cryptocurrency prices. Sole dependence on technical analysis with disregard for such factors often results in poorly assessed decisions in trading.
Solution: Integrate Fundamental Analysis
Couple your technical analysis with fundamental analysis, such as projections of fundamentals, adoption rates, the legal environment, and market sentiment. Combining your technical and fundamental views will help you make more informed decisions and avoid the trap of ignorance of the market context.
-
Over-trading and Too Much Screen Time
One of the most common problems traders encounter is over-trading due to catching themselves up with immediate responses to short-term movements in price and market noise.
Pitfall: Reacting to Every Price Fluctuation
Frequent buying and selling based on trivial price changes can easily lead to excessive transaction costs and increased losses. Over-trading often results from spending too much time on a screen and a desperate urge to participate in every market fluctuation.
Solution: Formulate a Trading Plan
Draw clear, specific trading plans with precise entry and exit levels. Clearly state your goals and stick with your strategy, avoiding spontaneous, unplanned trades based on fluctuations in the security price. Using larger time frames for analysis would be best since they will be less influenced by market noise, enabling you to focus better on more significant trends.
-
Misinterpreting Chart Patterns
Chart patterns offer great ways of making price forecasts; however, misinterpretations may be drawn from them.
Pitfall: Misreading Patterns
Chart patterns, such as head-and-shoulders, Double Tops, and Triangles, are subjective and sometimes variably formed. Misinterpreting them may lead to a bad trading decision.
Solution: Validate Patterns with Multiple Factors
Correctly identify and confirm chart patterns, including volumes and trendlines. To ensure your pattern analysis is credible, please have many confirmations from various sources, such as technical indicators, price action, etc.
-
Overcomplicating the Analysis
The second common mistake is overcomplicating the technical analysis by applying too many indicators and techniques.
Pitfall: Too Many Indicators
Too many indicators can lead to paralysis during analysis. Conflicting signals and complicated charts can make decision-making tricky, clutter your chart, and diminish clarity.
Solution: Key Indicators
Choose a few complementary indicators that give clear signals. Could you develop a simplified technical analysis system using indicators compatible with your trading methodology? This may enable you to make more accurate and potent trading decisions.
-
Forgetting About Risk Management
Poor risk management can bring huge losses even if the technical analysis is correct.
Pitfall: Risk Management Negligence
It is essential to manage your trading capital and minimize your losses. Failing to set stop-loss orders, position sizes, and risk-reward ratios can easily lead to disproportionate losses.
Solution: Apply a Risk Management Strategy
Your trading plan should include risk management techniques for capital protection and profit lock-in, such as stop-loss and take-profit levels. Could you designate the correct position sizes that fit your risk tolerance and ensure the risk-reward ratio aligns with your trading strategy?
-
Failing to Adapt to Changes in the Market Conditions
The cryptocurrency market is highly dynamic, where strategies that work during one market condition may not work during another.
Pitfall: Adhering to Outdated Strategies
Moreover, relying on strategies that worked in previous market conditions without adapting them to the current trend can lead to poor results. Market conditions change rapidly, altering the workability of technical analysis.
Solution: Be Flexible and Adapt
Periodically reassessing one’s trading strategies will also keep one in tune with prevailing market conditions. Being well-versed in market trends, news flow, and fundamental factors influencing your analysis will keep you open to change and flexible enough to adapt quickly to new techniques that work for you.
Conclusion
Technical analysis for crypto trading is an effective tool for demonstrating the right way to make trade decisions. However, it has its downsides. A trader who avoids mistakes such as dependence on too many indicators, ignoring market context, over-trading, incorrect interpretation of patterns, complication of analysis, not paying attention to risk management, and not adapting one’s approach given changed conditions will be able to make more assured improvements in his decision-making process and make a profit.
By integrating these means while remaining balanced in approach, you will be better positioned to handle the intricacies of the cryptocurrency market and thereby achieve better trading outcomes.
FAQ
- What is Technical Analysis in crypto trading?
Technical Analysis (TA) is a methodology for predicting the future. Movement of prices based on past market data. It analyzes the main volume of the trade. Therefore, TA helps a crypto trader identify patterns and trends to guide him in making informed decisions.
- How does Technical Analysis differ from Fundamental Analysis?
While technical analysis considers everything from price movements to market data, fundamental analysis concerns the very foundations-such as the project’s technology, its use cases, and the credibility of the team behind it, arriving at an approximation for the intrinsic value of an asset.
- What are some key crypto indicators?
It involves indicators such as the MA, RSI, MACD, and Bollinger Bands, which help one notice trends, momentum, and volatility.
- What are candlestick charts, and why are they used in crypto trading?
Candlestick charts are graphical representations of price movements over a specified period. They are applied in crypto trading for reasons that will be highlighted. Each candle shows the open, closing, high, and low prices; thus, traders can easily see patterns, such as trend reversals, the start of trends, or consolidation phases.
- How do I read the crypto chart trend line?
Trend lines are drawn by connecting the highs or significant lows in price movements. An upward-biased trend line indicates a bull market, while a downward-biased trend line indicates a bear market.
- What is the Return to Mean (RTM) Strategy?
The RTM strategy is based on the premise that price action will always revert to its mean or average after considerable deviation. Generally, traders look for periods of extreme prices and expect them to return to the mean level.
- Why Should Technical and Fundamental Analysis be combined?
Put together, they give an added insight into the market. If the technical analysis can help the individual decide on entry and exit points, fundamental analysis will aid in finding the long-term potential of the crypto asset.
- Can I Trade Solely Based on Technical Analysis?
Of course, some traders exclusively rely on Technical Analysis, especially for shorter-term trades. Theoretically, one would combine technical and fundamental analysis to determine a crypto asset’s broader context and longer-term prospects.
- What are some common mistakes in Technical Analysis?
Common pitfalls include overreliance on one indicator, missing the big picture in market trends, and using TA in isolation from external factors such as news or fundamental events in the crypto market.
- How to Avoid Fake Signals in Technical Analysis?
For that, several indicators must be combined and then cross-checked for signals. Proper knowledge of the market’s big picture and correct risk-management strategies involving stop-losses will also help limit potential losses.
- How often should I do Technical Analysis as a Crypto-Trader?
The frequency depends on your trading strategy. While day traders might do TA several times a day, the long-term investor may study charts once a week or even once a month.
- How can I improve my Technical Analysis?
That comes with practice. Devote your time to studying various charts, learning many indicators, and researching historical price patterns. You can also backtest strategies to see how they performed in the past.