Oracles in DeFi | As decentralized finance (DeFi) continues to revolutionize traditional financial architecture, one key but overlooked building block has a supporting role to play: oracles in DeFi. Oracles are the bridges between blockchain-based smart contracts and off-chain data, enabling accurate and dynamic decision-making. DeFi applications would be restricted to on-chain data without oracles, severely limiting their application.
In this beginner’s guide, we’ll explore what makes oracles in DeFi so crucial, how they function, and why they are the cornerstone of a secure and efficient decentralized ecosystem.
What Are Blockchain Oracles?
Blockchain oracles are platforms that serve as bridges between blockchains and off-chain data sources. Since blockchains are closed, they lack the capability to obtain off-chain data independently, such as real-world prices, weather, or sports scores.
Oracles are bridges used to introduce external data into smart contracts so that they can respond to off-chain occurrences in the real world. The concept of oracles in DeFi is essential since they allow one to introduce real-world data into permissionless financial systems.
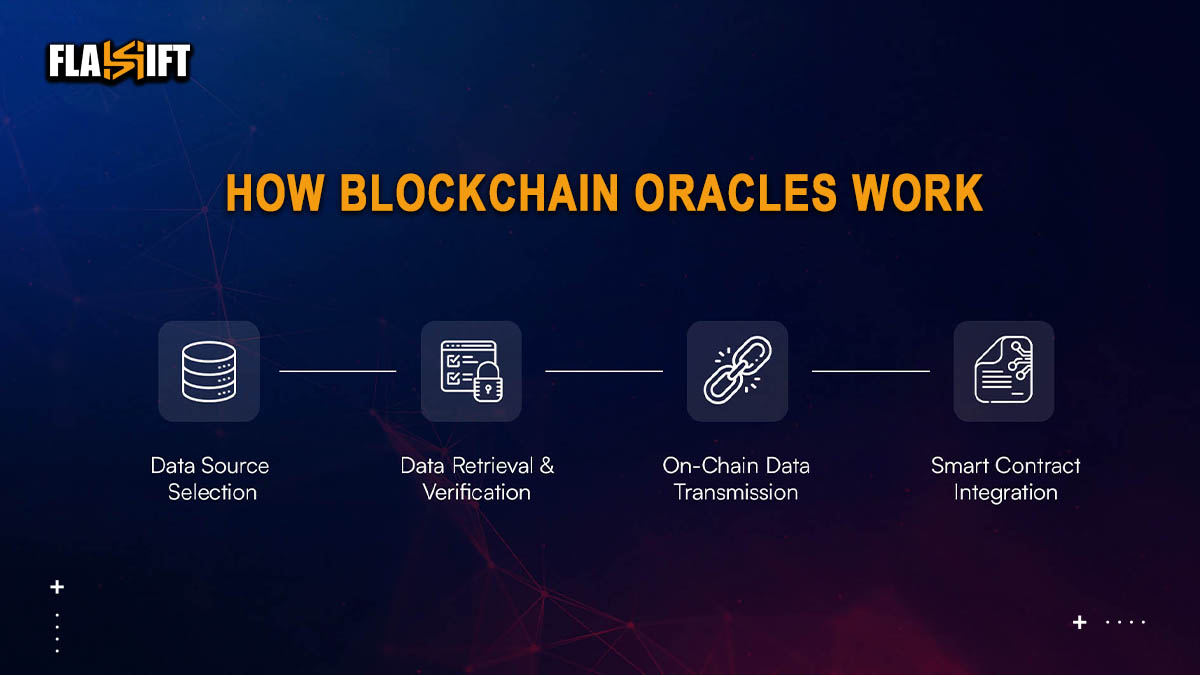
Why Oracles Are Needed in Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing programs that run on blockchains. Without oracles, blockchains’ functionality would be limited to on-chain logic. By providing accurate data inputs, oracles make smart contracts practical in real-world applications like insurance claims, supply chain tracking, and financial institutions. An oracle enables smart contracts to respond to real-time events like assets price movements or trading volume surges.
Types of Oracles: Software, Hardware, Inbound, and Outbound
- Software Oracles: Pull data from online sources like APIs, websites, or databases.
- Hardware Oracles: Feed data from physical sensors (e.g., IoT devices) into the blockchain.
- Inbound Oracles: Bring external data into smart contracts (e.g., asset prices).
- Outbound Oracles: Allow smart contracts to send data to external systems (e.g., initiating a bank transfer).
Each type of oracle in DeFi plays a specific role in enabling automated and accurate decision-making for decentralized applications.
Why Oracles Matter in DeFi

Decentralized finance (DeFi) relies on oracles to function effectively. Whether it’s calculating lending rates, triggering liquidations, or pricing synthetic assets, oracles provide the data backbone for DeFi protocols. An oracle ensures smart contracts operate with accurate and timely data inputs, maintaining trust and efficiency.
Use Cases in Lending, Trading, and Derivatives
- Lending Platforms (e.g., Aave, Compound): Use oracles to determine collateral value and liquidation thresholds.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Use price feeds for slippage protection and asset valuation.
- Derivatives Protocols: Need accurate asset data for settling contracts and managing risk.
Each use case showcases how an oracle in DeFi can support automation and transparency in decentralized financial systems.
Risks of Inaccurate Oracle Data (Oracle Problem)
Oracles can be targets for manipulation, leading to “Oracle attacks.” If a malicious actor feeds incorrect data, it could result in unfair liquidations, mispriced assets, or drained protocols. This is known as the “Oracle problem,” highlighting the need for secure and decentralized oracle solutions. Insecure oracles in DeFi become a single point of failure that could compromise the integrity of entire ecosystems.
Centralized vs Decentralized Oracles
- Centralized Oracles: Faster and easier to implement but create a single point of failure.
- Decentralized Oracles: More secure and transparent but can be slower and more complex to manage.
Choosing the right oracles in DeFi depends on your priorities—whether you value speed and simplicity or decentralization and resilience.
How ChainLink Became the Leading Oracle Solution

Chainlink is the most used decentralized Oracle network, with hundreds of DeFi protocols relying on it. It collects data from various sources and uses a decentralized node structure to provide security and high dependability by making manipulation impossible. As the top Oracle in DeFi, Chainlink provides secure and tamper-proof feeds for mission-critical applications.
Key Features of Chainlink’s Decentralized Oracle Network:
- Data Aggregation: Combines data from multiple sources to improve accuracy.
- Node Reputation System: Ensures reliable performance by rewarding honest behavior.
- Secure Hardware (e.g., Trusted Execution Environments): Prevent tampering and secure data delivery.
These features make Chainlink an ideal oracle in DeFi, setting the standard for how decentralized oracles should function.
Read More: How to Buy and Store ChainLink (LINK) in 2025
Real-World Integrations and Protocols Using Chainlink
Chainlink powers leading protocols such as Aave, Synthetix, and dYdX. It extends beyond DeFi into gaming, insurance, and traditional finance by enabling smart contracts to access verified real-world data. The platform’s widespread adoption proves its effectiveness as a top oracle in DeFi.
Which Is More Secure and Scalable?
Due to their resistance to censorship and manipulation, decentralized oracles are considered more secure for DeFi applications. However, scalability can be a challenge as they grow. Hybrid models combining both approaches are emerging as a practical solution. These models still rely on a strong oracle in DeFi to balance performance and decentralization.
The Future of Oracles in DeFi
As DeFi matures, oracles will become even more critical. Upcoming innovations include zero-knowledge-proof-based data verification, AI-enhanced data validation, and cross-chain oracle compatibility. Each new development will push the boundaries of what modern oracles in DeFi can achieve, making them smarter, faster, and more secure.
Expect to see a more regulatory focus on the data reliability layer, emphasizing the importance of trustworthy Oracle infrastructure. Without reliable oracles in DeFi, even the most sophisticated protocols are vulnerable to failure or exploitation.
Final Thoughts: Why Oracles Are the Backbone of DeFi
Without oracles, DeFi would not exist. Oracles enable smart contracts to interact with off-chain data and fill the gap between off-chain sources and blockchain. Understanding how oracles operate and how they ensure data integrity is essential to those exploring the world of DeFi today. Well-crafted oracles in DeFi protect users and ensure fairness, automation, and innovation across the ecosystem.
As DeFi has grown, the demand for more secure, decentralized, and quicker oracles will increase. Learning the structure of an oracle in DeFi opens your eyes to one of the most fundamental levels of Web3 infrastructure.
FAQ
- Can an oracle in DeFi operate without compromising user privacy?
Yes, emerging solutions like zero-knowledge proofs allow oracles to verify data without exposing user-specific details. - How do oracles handle conflicting data from multiple sources?
Decentralized oracles like Chainlink aggregate and weight inputs from multiple nodes to filter out anomalies and improve accuracy. - Are oracle fees a hidden cost in DeFi transactions?
Often yes. Some protocols pass oracle-related gas and service fees to users, subtly increasing transaction costs. - Can oracles be upgraded after deployment?
It depends. Some DeFi protocols use upgradeable contracts, while others fix oracle configurations for immutability and security. - How do oracles impact DeFi protocol governance decisions?
Reliable oracle data can trigger automated governance events, like pausing markets or adjusting parameters based on real-time risk.